Osteomyelitis In Sickle Cell Disease
Osteomyelitis in sickle cell disease. It is imperative to distinguish Salmonella osteomyelitis from bone infarctions. Acute osteomyelitis comprised 78 293 of the 266 major skeletal complications seen in 207 patients with sickle cell disease in a five and a half year period. Osteomyelitis of the mandiblein sickle cell disease A.
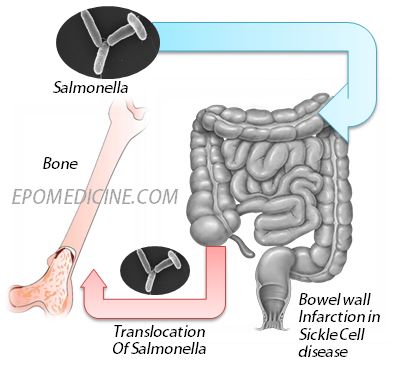
Patients with sickle cell disease are prone to infection of the bone and bone marrow in areas of infarction and necrosis. Salmonella osteomyelitis in sickle cell disease. In 1925 first identified the association of Salmonella osteomyelitis in sickle cell anemia patients.
Adekeye MaxillofacialUnit Departmentof Dental Surgery Ahmadu Bello University Hospital Kaduna Nigeria SUMMARYWe report 16 cases of osteomyelitis of the mandible in patients with sickle cell disease an incidence of 5 of all patients who presented with osteomyelitis of the jaws. The majority of Salmonella infections in sickle cell patients involve bones especially long bones and joints and occur most frequently in early childhood. Common organisms causing osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease Salmonella typhimurium Salmonealla enteritidis Salmonella choleraesuis Salmonella paratyphi B Staphylococcus aureus Hemophilus influenzae Escherichia coli Enterobacter spp.
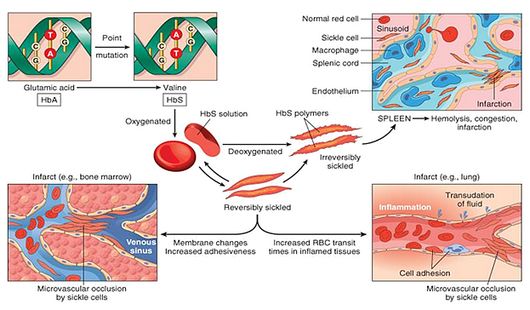
Burnett et al 1998 perhaps because intravascular sickling of the bowel leads to patchy. There are several sickle cell hemoglobinopathies namely HbSS HbSC and HbSthalassemia. Both sickle crisis and osteomyelitis may present with bone pain fever and leukocytosis and radiographs may be identical although patients with osteomyelitis have more severe symptoms.
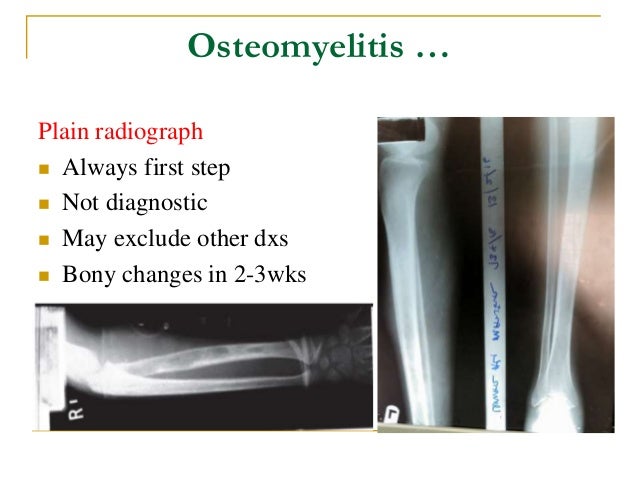
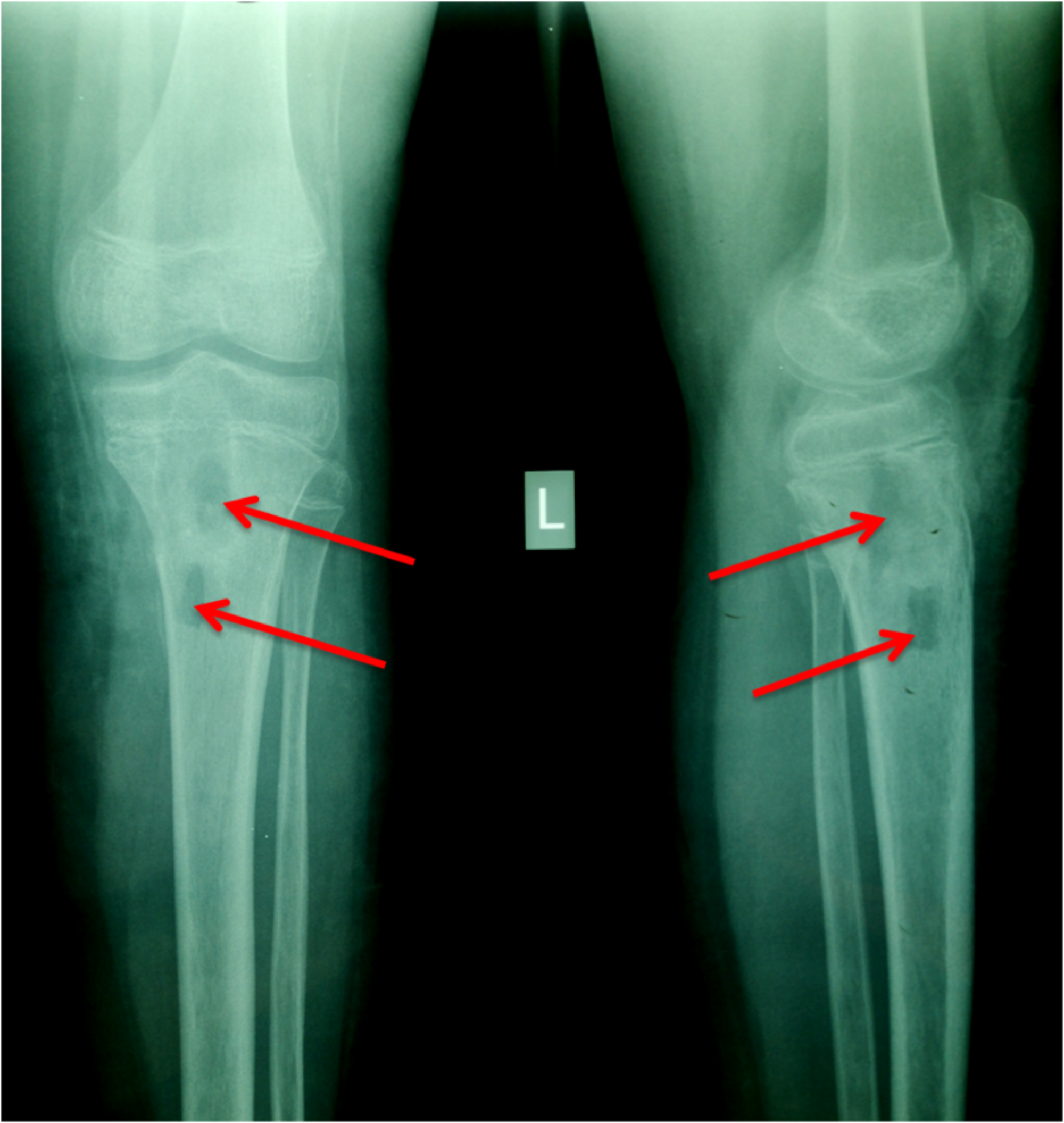
Before the appearance of the characteristic plain radiographic findings diagnosis of osteomyelitis in patients with sickle cell disease can be difficult because the clinical manifestations of infarction and osteomyelitis can be similar. Sickle cell disease SCD is a collective term for several genetic disorders in which hemoglobin is structurally abnormal resulting in the episodic formation of sickle-shaped red blood cells and a wide range of clinical manifestations. In sickle cell anemia an early detection and diagnostic accuracy of.
1 Infection is a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality in SCD. Radionuclide scans have yielded mixed results. In sickle cell anemia an early detection and diagnostic accuracy of osteomyelitis would establish an immediate treatment module for preventing bone destruction and deformity.
The most common cause of osteomyelitis is Staphylococcus aureus. Septicemia Cellulitis Septic arthritis- given the early decrease in splenic function bacterial infections of bone and joints are common in children with sickle cell disease Deep abscess Non-Infectious conditions.
Septicemia Cellulitis Septic arthritis- given the early decrease in splenic function bacterial infections of bone and joints are common in children with sickle cell disease Deep abscess Non-Infectious conditions.
Radionuclide scans have yielded mixed results. Salmonella osteomyelitis in sickle cell disease. Both sickle crisis and osteomyelitis may present with bone pain fever and leukocytosis and radiographs may be identical although patients with osteomyelitis have more severe symptoms. Osteomyelitis of the mandiblein sickle cell disease A. Presentation of osteomyelitis may be subtle mimicking sickle crisis or affecting multiple areas. There are several sickle cell hemoglobinopathies namely HbSS HbSC and HbSthalassemia. The most common cause of osteomyelitis in sickle cell disease is Salmonella especially the nontypical serotypes Salmonella typhimurium Salmonella enteritidis Salmonella choleraesuis and Salmonella paratyphi B followed by Staphylococcus aureus and Gramnegative enteric bacilli Atkins et al 1997. How does osteomyelitis present in Sickle Cell Disease. Osteomyelitis both acute and chronic is one of the most common infectious complications in people with sickle cell disease.
Distinguishing between acute presentations of osteomyelitis OM and vaso-occlusive crisis VOC bone infarction in children with sickle cell disease SCD remains challenging for clinicians particularly in culture-negative cases. Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis Vertebral compression fracture Vaso-occlusive. Sickle cell disease SCD is a collective term for several genetic disorders in which hemoglobin is structurally abnormal resulting in the episodic formation of sickle-shaped red blood cells and a wide range of clinical manifestations. Both sickle crisis and osteomyelitis may present with bone pain fever and leukocytosis and radiographs may be identical although patients with osteomyelitis have more severe symptoms. Although Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of osteomyelitis. AlDallal Haematology Laboratory Specialist Haematology Department Amiri Hospital Kuwait Abstract Osteomyelitis is an infectious stage of bones associated with distinct clinical microbiology. Presentation of osteomyelitis may be subtle mimicking sickle crisis or affecting multiple areas.




























Post a Comment for "Osteomyelitis In Sickle Cell Disease"